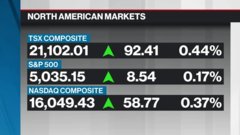
Feb 7, 2019
Aurora Innovation's self-driving dream team gets US$530M from Amazon, Sequoia
, Bloomberg News

The self-driving startup Aurora Innovation Inc. has raised US$530 million from a group of investors led by Sequoia Capital, Silicon Valley’s storied venture capital firm, that includes financial backing from Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN.O) and T. Rowe Price Group Inc. This second round of funding for Aurora values the company at more than US$2.5 billion.
Aurora’s three co-founders are legendary within the tight community of roboticists and engineers who are leading the charge to make self-driving cars a reality. Chris Urmson, the chief executive officer, was an early leader of the driverless car project launched within Google that later became Waymo, now widely seen as the first robotaxi business to emerge. Sterling Anderson, Aurora’s chief product officer, previously led Tesla Inc.’s (TSLA.O) Autopilot team that developed driver-assistance technology for the electric-car maker. Drew Bagnell, the chief technology officer, was a founding member of Uber’s Advanced Technologies Group.
The stature of its founders has allowed Aurora to attract top talent, with more than 250 people split between the San Francisco Bay Area and Pittsburgh, as well as interest from investors and partners. The startup has remained fiercely independent, cultivating partnerships with Hyundai Motor Co., Volkswagen AG and Byton Ltd. while designing a suite of software, hardware and data services designed to support a range of automakers and transportation networks. In a recent blog post, Aurora alluded to working with a fourth automaker but has not yet disclosed who it is.
The large investment by a group led by Sequoia, with T. Rowe Price and Amazon involved, will count as a vote of confidence in a competition between driverless efforts that’s largely measured in funding and alliances. “Over the last couple of years, we’ve met with more than 15 of the top autonomous vehicle companies from around the world,” said Sequoia’s Carl Eschenbach in an interview. “This is the dream team of self driving vehicles. Aurora has the best team across the industry and the best shot of being the most disruptive force going forward.”
The new round of funding will allow Aurora to continue to scale its operations. Eschenbach will take a seat on the startup’s board.
“This is really about accelerating and delivering on our mission, which is to deliver self-driving technology safely, quickly and broadly,” Urmson said in an interview. “We’ve been incredibly fortunate that there is a lot of interest in Aurora, and we have been able to pick who is the most strategic for us.”
In California, which has become the global center of autonomous-vehicle research, at least 62 companies have permits to test cars from the state Department of Motor Vehicles. But the crowded field is largely dominated by the top five companies with significant backing and funding: Alphabet Inc.’s Waymo unit, General Motors Co.’s Cruise unit, Zoox, Aurora and Ford Motor Co.-backed Argo AI.
Those self-driving frontrunners are making their own moves. On the recent earnings call of Waymo’s parent, Alphabet CFO Ruth Porat said the company is in talks to move into several other cities beyond the Phoenix area, where its first robotaxi service debuted in late 2018. GM CEO Mary Barra said the carmaker will spend about US$1 billion on Cruise in 2019 during Wednesday’s earnings call. Investments last year from the SoftBank Vision Fund and Honda Motor Co. pushed Cruise’s valuation to US$14.6 billion. Zoox raised US$500 million last summer and recently announced former Intel Corp. executive Aicha Evans as its new CEO.
But despite the money pouring into the industry, the self-driving cars that are common on the streets of Silicon Valley are largely test vehicles with safety drivers behind the wheel. Even Waymo’s robotaxi service in Arizona still has trained backup drivers inside.
The fact that Aurora drew investment from Amazon, which hasn’t made many high-profile moves into driverless vehicles, will invite speculation about the online giant’s motivations. “Autonomous technology has the potential to help make the jobs of our employees and partners safer and more productive,” an Amazon spokesperson said, “whether it’s in a fulfillment center or on the road, and we’re excited about the possibilities.”
Self-driving cars are not just for people— the technology can also move goods. Amazon currently uses automation in its warehouses and is designing a future delivery system with drones to deliver packages, and is a technology company with a significant logistics arm. Waymo has been in talks to create a delivery and logistics effort, while Ford has been testing driverless delivery of pizza with Domino’s and groceries with Postmates.
T. Rowe Price, another new investor in Aurora, is Tesla’s second-largest shareholder after Chief Executive Elon Musk, according to Bloomberg data. “The team at Aurora has unparalleled experience and expertise in solving the challenge of autonomous driving,” said Paul Greene, a portfolio manager for the Baltimore-based investment firm’s communications and technology fund.
This year will mark a public test for some of the early leaders in driverless technology. In addition to Waymo’s attempt push into new cities, GM’s Cruise is fine-tuning safety issues before a planned launch of a driverless ride-hailing service before the year ends.
For Aurora’s Urmson, who has been working on the technology for more than a decade, this isn’t a race: “We’re clear with our investors that this is a long road,” he said, “and at the end of that road is incredible impact on improving safety and mobility.”