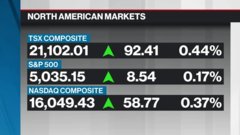
Dec 21, 2021
Investing in Chips
, Bloomberg News
(Bloomberg) -- Stay on top of the revolutions reshaping the auto world — from EVs to self-driving technology — by signing up for Hyperdrive’s newsletter here.
A Chinese proverb goes, “If you have guanxi (relations) with very important people, all your troubles will go away, but if you don’t have any guanxi with any VIP, your troubles will continue to haunt you.”
Carmakers seem to be embracing the proverb as they continue to confront and struggle with the persistent chip shortage that’s expected to cost them more than $200 billion in sales this year. The shortage hit in late 2020; heading into the new year, few foresaw it extending into 2023, as many in the chip industry now expect.
Before the pandemic, carmakers used to rely on what they referred to as their “tier one” suppliers to deal with semiconductor providers. Now they are racing to cozy up to the companies that produce physical chips for everything from smartphones to vehicles, striking partnerships and deals to lock in direct supply lines. Competition remains stiff, as mobile technology chip designers, typically favored by foundries over auto customers, are aggressively moving to lock in sufficient supply. Some of recent auto industry moves include:
- In early December, BMW AG signed an agreement with Inova Semiconductors and GlobalFoundries Inc., guaranteeing the supply of “several million” chips per year.
- Ford has forged a “strategic collaboration” with GlobalFoundries to explore buying directly from the U.S.-based chipmaker.
- General Motors Co. is planning to jointly create chips with producers including Infineon Technologies AG and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co.
- Stellantis NV has inked a deal with Foxconn Technology Group to develop automotive chips together. Foxconn, the top assembly partner to Apple Inc., is not exactly a major semiconductor player, though its familiarity with Taiwanese contract chipmakers may help Stellantis with component procurement.
- SAIC Motor Corp’s investment arm went a step further, investing 500 million yuan in auto chip startup GTA Semiconductor Co.
Even Tesla reportedly was exploring the option of buying a chip plant, according to news reports last spring. An overreaction? Maybe at the time but throughout 2021, car makers across the globe were forced to suspend manufacturing operations because of low supplies. They’re determined to avoid such moves in the years ahead.
“We are even talking to our vendors about our plans for the next two, three, four years,” President Joe Chen of MediaTek Inc., a major mobile chip supplier to Chinese smartphones brands including Xiaomi Corp., told reporters on Dec. 16. Some are calling this approach to secure and stockpile chips “just-in-case,” a shift from the pre-pandemic “just-in-time” model that relied on a thin inventory to drive profitability. The updated inventory management practice could last for a while, as some semiconductor makers, including Intel Corp., are suggesting the chip crunch could last into 2023.
Car companies eventually might adopt a hybrid approach when supply and demand regain some balance, considering that the shelf life of certain chips is short. “Many components especially high value components don't age well,” JP Morgan analyst Gokul Hariharan said in an interview in November. “Once the market comes into balance in 18 months, the industry might move back to elements of the ‘just in time’ model again.”
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.