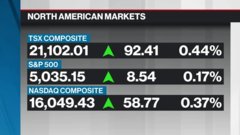
Sep 4, 2021
Auto Shows Are Back and CEOs Have Wheeling-and-Dealing to Do
, Bloomberg News
(Bloomberg) -- When automotive chieftains gather in Munich this upcoming week for Europe’s first major car show in two years, they’ll do more than just lift the veil on shiny sheet metal. These are occasions where big deals tend to get done.
Consider one of the last times the auto world descended on a European city for such a forum in March 2019. Just before the action got underway in Geneva, the CEOs of Peugeot maker PSA and Fiat Chrysler met to sow the seeds of what blossomed into a mega merger, vaulting Stellantis NV into the same league as Toyota Motor Corp. and Volkswagen AG.
There’s no telling whether executives will mask-up and elbow-bump their way to another blockbuster transaction in Munich. Toyota, Stellantis and Nissan Motor Co. aren’t even attending, and carmakers that are will send smaller contingents due to the surging delta variant. If that weren’t enough, many who want to get to Bavaria have had their travel plans disrupted by a Germany-wide rail strike.
Still, this much is certain: the same forces that drove PSA and Fiat into one another’s arms are only more relevant two years after their initial huddle off the 2019 Geneva show floor.
“You’ve got to be innovative, and for that you need to have significant firepower and a global footprint,” said Peter Fuss, a partner at EY. “Otherwise, the dependence on certain markets is too great and there’s the issue of scaling technologies.”
Carmakers have earmarked a whopping $330 billion in spending to electrify their lineups by 2025, according to consultants at AlixPartners. Revenue is being constrained by the global semiconductor shortage that is showing no signs of letting up anytime soon. Charging infrastructure must be built out to ensure EVs will appeal to the masses. And while sales of battery-powered cars are starting to take off, catching up with tech giants in the race to bring autonomous driving and connectivity to cars will be a herculean task.
Read more from QuickTake:
- Driverless? No, But How About the Car as Co-Pilot?
- Where We Are on the Road to Electric Vehicles?
VW CEO Herbert Diess in June called driverless vehicles “the most sophisticated internet device you can imagine,” predicting autonomy will bring about even greater change to the industry than the rise of EVs. Carmakers accustomed to competing on zero-to-60 times and other specs are now battling for valuable in-car data with deep-pocketed tech firms. At stake is control over what could become a $400 billion market by 2030, according to McKinsey & Co.
Pursuing tie-ups and M&A will be essential, EY’s Fuss said, because carmakers “rightly sense” they’re moving too slowly. While VW is plotting a more than $30 billion software-related investment binge, even Diess has said there are old, encrusted structures the company must dismantle in order to be more agile.
He and his peers better hurry. Amazon.com Inc. has demonstrated its mobility ambitions by backing electric-vehicle maker Rivian Automotive Inc. and snapping up self-driving startup Zoox. Google has had its struggles scaling its autonomy efforts, but it remains widely viewed as the leader in the space. Speculation was rampant early this year that Apple Inc.’s car activities are picking back up.
Plenty Activity
Europe’s carmakers are already doing plenty of wheeling-and-dealing to combat the threats. Just this year, VW has kicked the tires on a potential listing of Porsche and handed off majority control of Bugatti. Daimler is breaking itself up into separately listed truck and car companies, its biggest shake-up since the sale of Chrysler.
Outside Germany, Renault SA is working to fill what its CEO has described as an unacceptable void in China by joining forces with Geely Holding Group. Geely, meanwhile, is exploring a listing of Volvo Cars later this year, and their EV-making offshoot Polestar is said to have discussed going public through a blank-check firm merger that could value the company at $25 billion.
The car-parts sector also has been plenty active. France’s Faurecia SE just prevailed in a bidding battle with peers for Germany’s Hella GmbH in an $8 billion deal that was one of the biggest among European auto suppliers in years. Sweden’s Veoneer Inc. is poised to end up in the hands of Qualcomm Inc. or Magna International Inc. And Vitesco Technologies, the powertrain and sensor unit due to be spun off from Continental AG this month, has already flagged its appetite for M&A.
‘Terrifying’ Trend
While auto shows have been ideal forums for deal-making, prospects may be better for shows after Munich. Business travel remains in pandemic-induced doldrums, and in Germany -- where six-in-10 people are fully vaccinated -- the infection rate has managed to surge fivefold in the past month.
While organizers for the show this upcoming week are banking on outdoor spaces and inner-city events helping to open up space for participants to spread out, some executives remain concerned. Audi is staffing the show with a small team and reducing its trade-fair presence to a single outdoor stand, according to CEO Markus Duesmann.
“It’s terrifying -- for us all, I believe -- how the incidence rates are developing, and we know that hospitalizations and rising deaths normally follow,” he told reporters last week. “I like the concept, but I see the timing critically because of the incidences.”
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.