Dec 9, 2021
As Libor Goes Away, U.S. Replacement Makes a Big Trader Uneasy
, Bloomberg News
(Bloomberg) -- Dollar Libor’s fate is set: It will no longer be available for new loans and other products starting on Jan. 1, mostly replaced by the benchmark that regulators want.
But that doesn’t mean everybody loves the Secured Overnight Financing Rate, the leading U.S. alternative.
Take Don Wilson, founder of Chicago-based trading firm DRW, which will play a big role in the Libor-to-SOFR transition since his company trades derivatives tied to both rates. He thinks regulators made a mistake promoting SOFR as the right solution for everyone.
The problem, according to Wilson, is that SOFR will do a poor job hedging risks in turbulent times.
“For somebody who wants to hedge their borrowing costs, it leaves a lot to be desired,” Wilson said in a recent interview. “It’s a great product as long as credit spreads remain static. The time it really falls apart is in a crisis.”
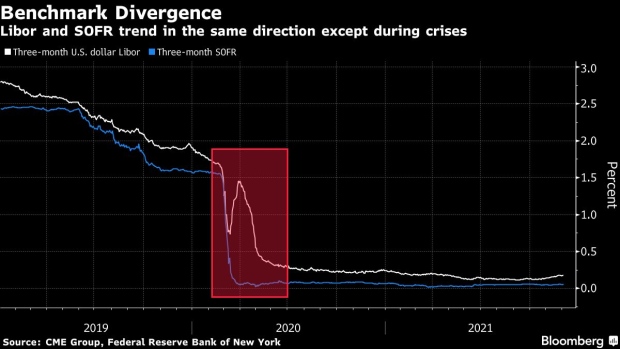
The early days of the pandemic help illustrate that. When Covid fear ripped through markets in 2020, three-month Libor spiked as lending markets locked up. But the comparable SOFR fell, dragged lower by the Federal Reserve slashing interest rates. In other words, SOFR didn’t reflect just how challenging credit markets were.
Wilson’s critique isn’t new and he’s not alone. SOFR has been dogged with complaints since the Fed-backed Alternative Reference Rates Committee anointed it as the new benchmark for key dollar markets more than four years ago.
U.S. officials continue to stand behind SOFR, arguing it’s a robust rate built on huge trading volume.
SOFR is calculated using transactions on overnight repurchase agreements, or loans collateralized by U.S. Treasuries. As a result, it tends to follow whatever the Fed is doing with interest rates, ignoring -- to some extent -- whatever stresses there might be in credit markets. When the Fed cuts rates, as it often does during a crisis, that should pull SOFR down.
But that means it won’t really work for someone trying to hedge credit risks. Libor tends to jump during a crisis, meaning it’s useful for that purpose.
“When there is stress on the financial system, that’s when it’s really going to fall short,” Wilson said. “Which, of course, if we’re concerned about the resilience of the system, we need to make sure that your hedging products especially work during that period. Because that’s when they’re most critical.”
Wilson’s firm is a major market maker in Eurodollar derivatives, which are tied to Libor, and also trades SOFR contracts, so DRW will be involved regardless.
Regulators, he said, have “decided they want everyone to use SOFR. I cannot explain it.”
Elsewhere in credit markets:
Americas
A risk-off tone Thursday morning in New York slowed debt issuance after U.S. investment-grade sales set a new December record on Wednesday and the junk market posted its busiest session by deal count in nearly a month.
- Media and technology company Yahoo’s $300 million leveraged loan is among at least 12 deals due Thursday
- The U.S. House approved legislation designed to protect trillions of dollars of assets from chaos when Libor expires, in one of the final key steps aimed at guaranteeing an orderly transition from the discredited benchmark
- For deal updates, click here for the New Issue Monitor
- For more, click here for the Credit Daybook Americas
EMEA
Sovereign and public sector issuers have set out plans for next year to raise debt in the capital market.
- France is targeting 260 billion euros of sales in 2022, while Belgium expects 48 billion euros of gross borrowing needs
- Denmark is planning a green bond in January, and the European Stability Mechanism/European Financial Stability Facility group is thinking of raising 27.5 billion euros
- Successful bond sales this week is a positive sign for Europe’s new issues market, as spreads recover from the omicron shock
- Read more: Safe Credit Bets Offer Incomplete Prelude to Next Year’s Demand
- There are possible indications for a further series of the ECB’s targeted longer-term refinancing operations at present, according to Norddeutsche Landesbank - Girozentrale
Asia
Asian dollar bonds continued to rally Thursday after the PBOC’s decision to inject liquidity into its domestic market eased concerns about a potential fallout in its property sector.
- Focus is on Kaisa Group Holdings Ltd., which is on the brink of becoming the second major Chinese developer to renege on debt obligations this week.
- A group of Kaisa bondholders is close to signing non-disclosure agreements with the developer in a move that would pave the way for discussions around a potential financing deal for the beleaguered firm
- Australia debt market is showing signs of stress amid concerns the Reserve Bank of Australia’s bond purchases are hampering trading
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.