Mar 1, 2021
U.S. Manufacturing Expands Most in Three Years as Prices Climb
, Bloomberg News
(Bloomberg) -- U.S. manufacturing expanded in February at the fastest pace in three years and a gauge of materials costs accelerated the most since 2008 as supply shortages challenge the industry.
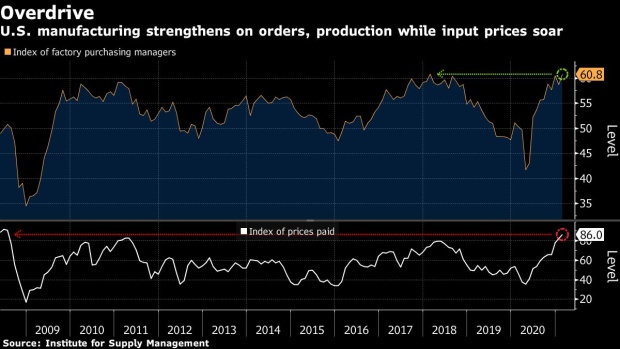
A gauge of factory activity increased to 60.8 from 58.7 a month earlier, according to Institute for Supply Management data released Monday. Readings above 50 indicate expansion and the figure exceeded the 58.9 median estimate in a Bloomberg survey of economists.
At a time when household and business demand is off to a solid start to the year amid lean inventories, producers are struggling with rising costs for raw materials, labor force disruptions and higher shipping rates. The ISM’s measure of prices paid for inputs climbed nearly 4 points in February to 86, the highest since July 2008.
Orders, production and factory employment measures all expanded at faster paces last month, highlighting robust and resilience in manufacturing that’s helping power the economy. At the same time, a measure of unfilled orders surged to the highest level in nearly 17 years while another gauge showed delivery times were the second-longest since 1979.
“Labor-market difficulties at panelists’ companies and their suppliers continued to restrict manufacturing-economy expansion and will remain the primary headwind to production growth until employment levels and factory operations can return to normal across the entire supply chain,” Timothy Fiore, chair of ISM’s Manufacturing Business Survey Committee, said in a statement.
The group’s gauge of order backlogs advanced to 64 last month, the highest since April 2004 and its index of supplier deliveries jumped almost 4 points to 72.
Shortages of semiconductors have idled production at some auto plants. The disruption in supplies is largely tied to the pandemic as more people began working from home, spurred sharp increases in demand for electronics and computers.
Select ISM Industry Comments
“Things are now out of control. Everything is a mess, and we are seeing wide-scale shortages.” - Electrical Equipment, Appliances
“Supply chains are depleted; inventories up and down the supply chain are empty. Lead times increasing, prices increasing, (and) demand increasing.” - Chemical Products
“Steel prices have increased significantly in recent months, driving costs up from our suppliers and on proposals for new work that we are bidding.” - Transportation Equipment
“We are still struggling keeping our production lines fully manned.” - Food, Beverage & Tobacco Products
“Logistics times are at record times. Continuing to fight through shipping and increased lead times on both raw materials and finished goods due to the pandemic.” - Fabricated Metal Products
“Prices are rising so rapidly that many are wondering if (the situation) is sustainable. Shortages have the industry concerned for supply going forward, at least deep into the second quarter.” - Wood Products
Sixteen of 18 manufacturing industries reported growth in February, led by textiles, electrical equipment and appliances, and primary metals.
Production, Orders
The ISM index of production rose 2.5 points in February to 63.2, while the new orders’ gauge climbed 3.7 points to 64.8.
To help meet demand, factories are adding to headcounts, the report showed. An index of manufacturing employment increased to the highest level in almost two years.
A survey of economists by the National Association for Business Economics showed increased optimism about the economy’s prospects this year. Respondents boosted their growth estimates for each quarter this year, according to the NABE report issued Monday.
Economists also forecast lower unemployment rates each quarter compared with their December projections.
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.